Connect a frontend
This guide describes how to create a frontend or client app that interacts with a node which is connected to a blockchain network.
| This guide covers how to build a frontend based on the Create React App guide to create a frontend application. |
Create project structure
| See the full code example of Hello World in GitHub. |
$ tree -I 'node_modules|client/node_modules|react-client/node_modules'
.
├── README.md
├── index.js
├── logs
│ ├── devnet
│ │ ├── lisk.log
│ │ └── lisk_db.log
│ └── lisk_db.log
├── package-lock.json
├── package.json
├── react-client
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── bufferFix.js
│ ├── package-lock.json
│ ├── package.json
│ ├── readBigUInt64BE.js
│ ├── src
│ │ ├── accounts.json
│ │ ├── api.js
│ │ ├── assets
│ │ ├── components
│ │ │ ├── Accounts.js
│ │ │ ├── App.js
│ │ │ ├── Blocks.js
│ │ │ ├── Faucet.js
│ │ │ ├── Hello.js
│ │ │ ├── HelloAccounts.js
│ │ │ ├── HelloTransactions.js
│ │ │ ├── NewAccount.js
│ │ │ ├── Transactions.js
│ │ │ ├── Transfer.js
│ │ │ └── home.js
│ │ ├── index.html
│ │ └── index.js
│ ├── test.js
│ └── webpack.config.js
└── transactions
├── hello_transaction.js
├── index.js
├── package-lock.json
├── package.json
└── test
└── hello_transaction.test.js
Setup
Install and run backend
Install
Firstly, please ensure you have all Lisk SDK dependencies installed, and have a fresh database lisk_dev.
| Dependencies | Version |
|---|---|
Node.js |
v12 (LTS) |
PostgreSQL |
10+ |
Redis (optional) |
5+ |
Python |
2 |
Clone the lisk-sdk-examples in GitHub and navigate into hello_world folder.
git clone https://github.com/LiskHQ/lisk-sdk-examples.git
cd lisk-sdk-examples/hello_world
git checkout v4
npm iInstall and run the frontend
Install
Next, install all dependencies for the react-client application:
cd react-client
npm iRun
Now start the web server:
npm start
#lisk_passphrase@1.0.0 start /Users/lisk/git/lisk-sdk-examples/hello_world/react-client
#webpack-dev-server --mode development --open --hot
#ℹ 「wds」: Project is running at http://localhost:8080/
#ℹ 「wds」: webpack output is served from /
#ℹ 「wds」: Content not from webpack is served from /Users/lisk/git/lisk-sdk-examples/hello_world/react-client
#ℹ 「wdm」: wait until bundle finished: /
#ℹ 「wdm」: Hash: d2ee0ce167dae52e5642
#Version: webpack 4.44.1
#Time: 5108ms
#Built at: 08/19/2020 1:49:13 PMThis will open the client app in the browser, under http://localhost:8080.
At this point it should now be possible to see a basic frontend for the Hello World application, that allows users to perform the following tasks:
| Use this client as a template or reference for your own client applications, and adjust it accordingly to suit your requirements. |
React app
The react app starts from index.js and renders the App component inside of the body tag of index.html.
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import App from "./components/App.js";
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById("root"));<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Lisk SDK example</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
</html>The main component is App.js.
It imports all other components and defines the Routes for the components.
import React from "react";
import {
BrowserRouter as Router,
Switch,
Route,
Link
} from "react-router-dom";
import "regenerator-runtime/runtime.js";
import NewAccount from './NewAccount';
import Accounts from './Accounts';
import HelloAccounts from './HelloAccounts';
import Faucet from './Faucet';
import SendTransfer from './Transfer';
import SendHello from './Hello';
import Transactions from './Transactions';
import HelloTransactions from './HelloTransactions';
import Blocks from './Blocks';
import Home from './home';
// The pages of this site are rendered dynamically
// in the browser (not server rendered).
export default function App() {
return (
<Router>
<div>
<Route>
<ul>
<li><Link to="/">Home</Link></li>
<hr />
<h3> Interact </h3>
<li><Link to="/new-account">New Account</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/faucet">Faucet</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/send-transfer">Send tokens</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/send-hello">Send Hello</Link></li>
<hr />
<h3> Explore </h3>
<li><Link to="/accounts">Accounts</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/hello-accounts">Hello accounts</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/transactions">Transactions</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/hello-transactions">Hello transactions</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/blocks">Blocks</Link></li>
</ul>
</Route>
{/*
A <Switch> looks through all its children <Route>
elements and renders the first one whose path
matches the current URL. Use a <Switch> any time
you have multiple routes, but you want only one
of them to render at a time
*/}
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/">
<Home />
</Route>
<Route path="/new-account">
<NewAccount />
</Route>
<Route path="/faucet">
<Faucet />
</Route>
<Route path="/send-transfer">
<SendTransfer />
</Route>
<Route path="/send-hello">
<SendHello />
</Route>
<Route path="/accounts">
<Accounts />
</Route>
<Route path="/hello-accounts">
<HelloAccounts />
</Route>
<Route path="/blocks">
<Blocks />
</Route>
<Route path="/transactions">
<Transactions />
</Route>
<Route path="/hello-transactions">
<HelloTransactions />
</Route>
</Switch>
</div>
</Router>
);
}API client
It is recommended to define the API client in a single file, and import it where required.
If the API url changes in the future, it is only required to update the API_BASEURL.
import { APIClient } from '@liskhq/lisk-api-client';
const API_BASEURL = 'http://localhost:4000';
export const api = new APIClient([API_BASEURL]);The API client will be imported into the necessary components shown below:
Pages
Implement the logic and structure of the different pages of the client app.
Home
The start page of the Hello World app.
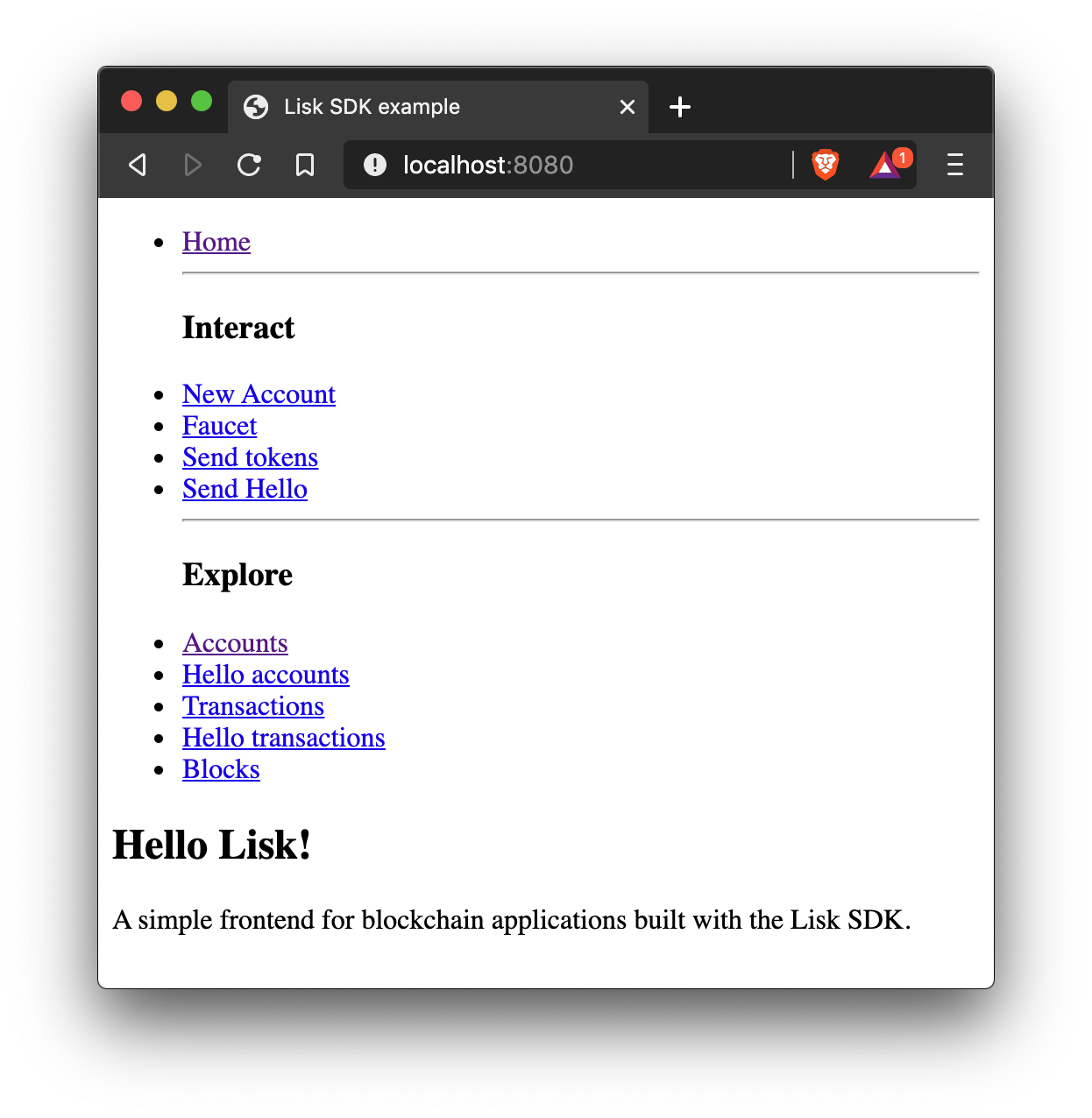
import React from 'react';
const Home = () => {
return (
<div>
<h2>Hello Lisk!</h2>
<p>A simple frontend for blockchain applications built with the Lisk SDK.</p>
</div>
);
};
export default Home;New account
This page generates the credentials for a new account in the network.
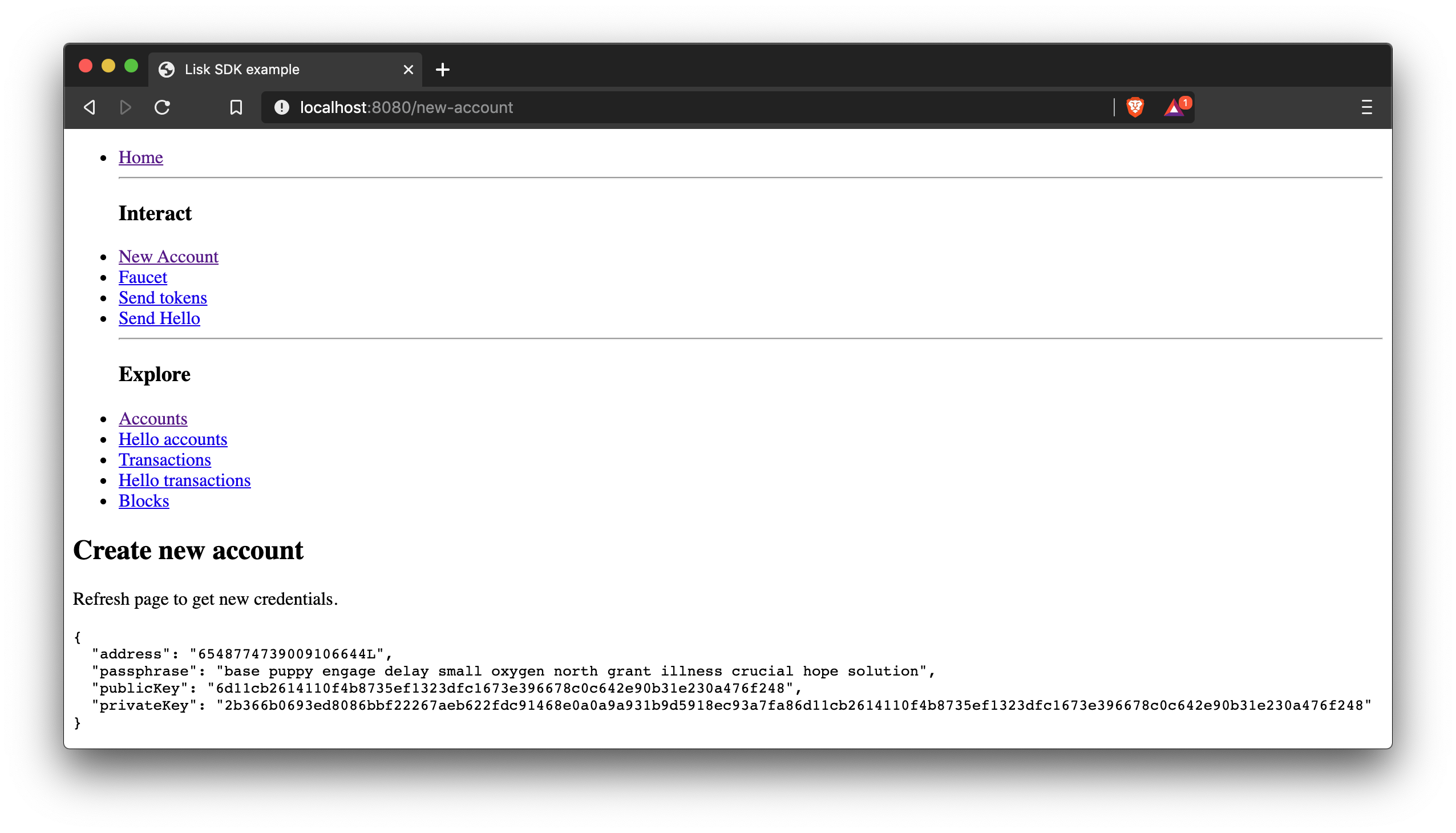
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { passphrase, cryptography, Buffer } from '@liskhq/lisk-client';
const newCredentials = () => {
const pass = passphrase.Mnemonic.generateMnemonic();
const keys = cryptography.getPrivateAndPublicKeyFromPassphrase(pass);
const credentials = {
address: cryptography.getAddressFromPublicKey(keys.publicKey),
passphrase: pass,
publicKey: keys.publicKey,
privateKey: keys.privateKey
};
return credentials;
};
class NewAccount extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { credentials: newCredentials() };
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>Create new account</h2>
<p>Refresh page to get new credentials.</p>
<pre>{JSON.stringify(this.state.credentials, null, 2)}</pre>
</div>
);
}
}
export default NewAccount;Faucet
A faucet is usually connected to a well funded account in the network, that is used as the source to send funds to accounts in order to get started. It is therefore primarily useful for Devnets or Testnets.
In this example, the genesis account is used in the faucet. In order to simplify this, no restrictions are set for the maximum amount and the frequency of requesting new tokens.
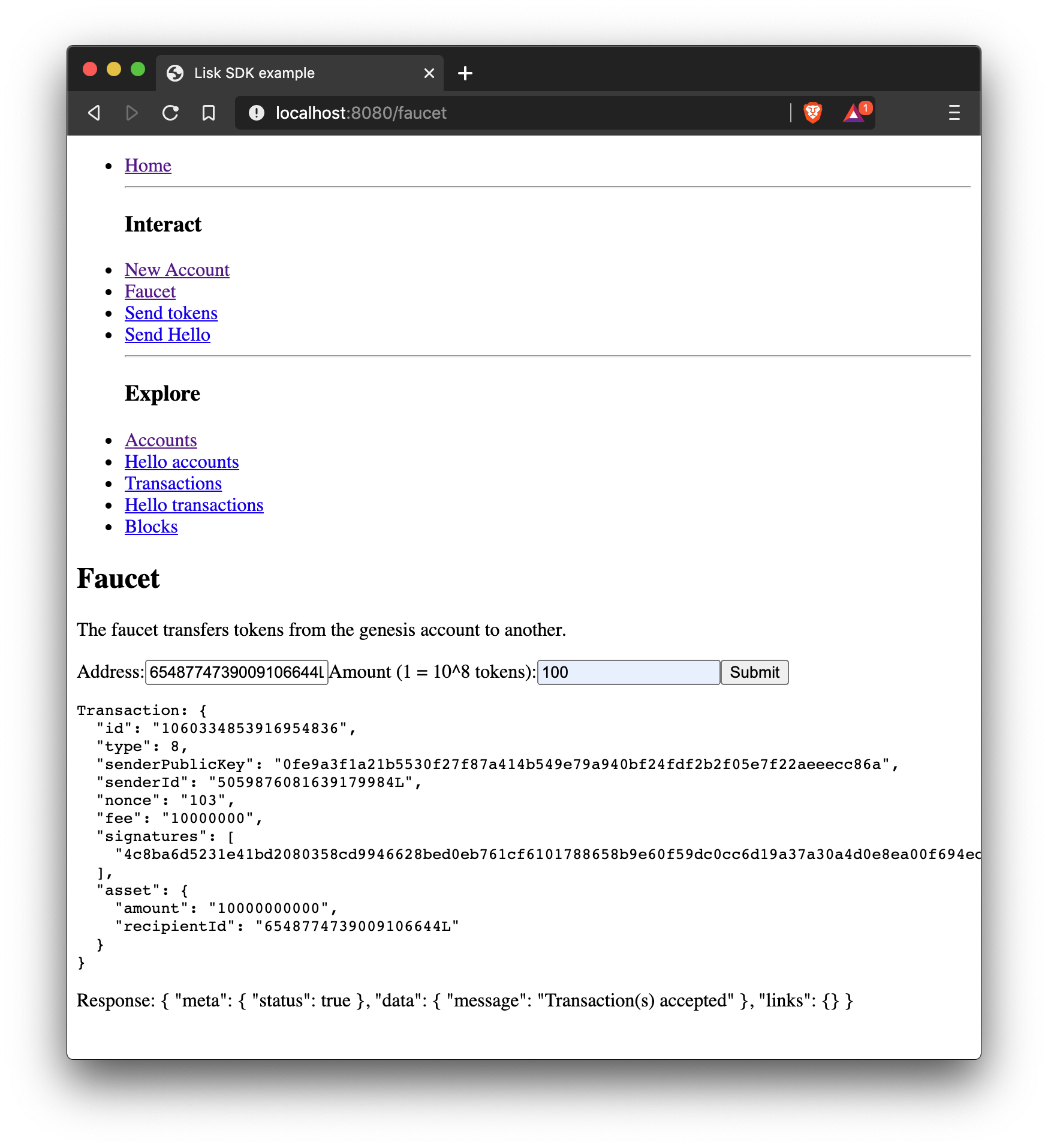
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { api } from '../api.js';
import accounts from '../accounts.json';
import{ transfer, utils } from '@liskhq/lisk-transactions';
import * as cryptography from '@liskhq/lisk-cryptography';
const networkIdentifier = cryptography.getNetworkIdentifier(
"19074b69c97e6f6b86969bb62d4f15b888898b499777bda56a3a2ee642a7f20a", //payloadHash
"Lisk", //Community Identifier
);
class Faucet extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
address: '',
amount: '',
response: { meta: { status: false }},
transaction: {},
};
}
handleChange = (event) => {
let nam = event.target.name;
let val = event.target.value;
this.setState({[nam]: val});
};
handleSubmit = (event) => {
event.preventDefault();
api.accounts.get({address: accounts.genesis.address}).then(response1 => {
const nonce = parseInt(response1.data[0].nonce);
const fundTransaction = transfer({
amount: utils.convertLSKToBeddows(this.state.amount),
recipientId: this.state.address,
passphrase: accounts.genesis.passphrase,
networkIdentifier,
fee: utils.convertLSKToBeddows('0.1'),
nonce: nonce.toString(),
});
//The TransferTransaction is signed by the Genesis account
api.transactions.broadcast(fundTransaction).then(response2 => {
this.setState({response:response2});
this.setState({transaction:fundTransaction});
}).catch(err => {
console.log(JSON.stringify(err.errors, null, 2));
});
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>Faucet</h2>
<p>The faucet transfers tokens from the genesis account to another.</p>
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<label>
Address:
<input type="text" id="address" name="address" onChange={this.handleChange} />
</label>
<label>
Amount (1 = 10^8 tokens):
<input type="text" id="amount" name="amount" onChange={this.handleChange} />
</label>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form>
{this.state.response.meta.status &&
<div>
<pre>Transaction: {JSON.stringify(this.state.transaction, null, 2)}</pre>
<p>Response: {JSON.stringify(this.state.response, null, 2)}</p>
</div>
}
</div>
);
}
}
export default Faucet;Send default transaction
How to send a default transaction from a web page.
In the example shown below, a transfer transaction is sent.
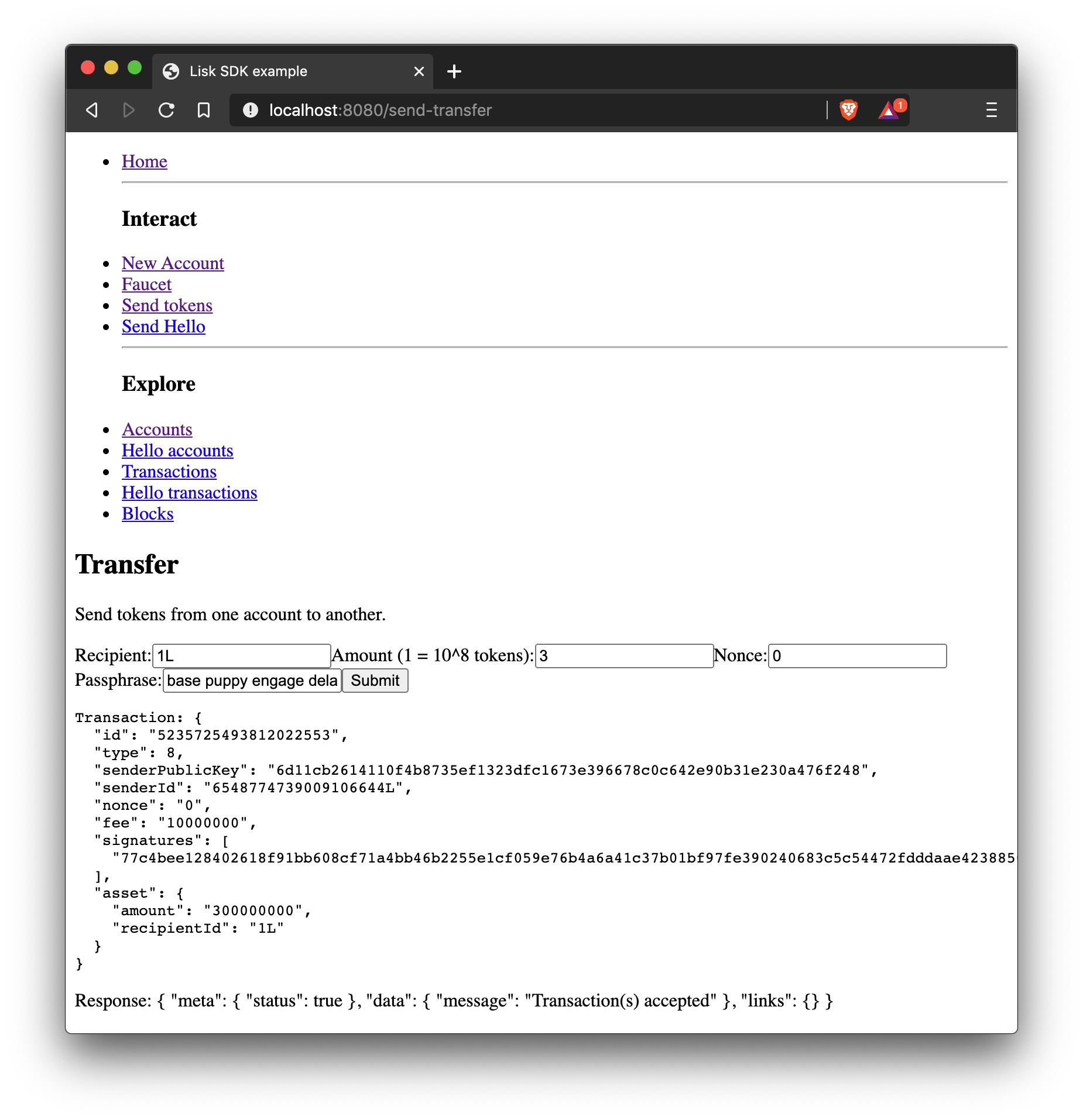
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { api } from '../api.js';
import { cryptography, transactions } from '@liskhq/lisk-client';
import {transfer, utils} from "@liskhq/lisk-transactions";
import accounts from "../accounts";
const networkIdentifier = cryptography.getNetworkIdentifier(
"19074b69c97e6f6b86969bb62d4f15b888898b499777bda56a3a2ee642a7f20a",
"Lisk",
);
class Transfer extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
address: '',
amount: '',
nonce: '',
passphrase: '',
response: { meta: { status: false }},
transaction: {},
};
}
handleChange = (event) => {
let nam = event.target.name;
let val = event.target.value;
this.setState({[nam]: val});
};
handleSubmit = (event) => {
event.preventDefault();
const transferTransaction = new transactions.TransferTransaction({
asset: {
recipientId: this.state.address,
amount: transactions.utils.convertLSKToBeddows(this.state.amount),
},
fee: utils.convertLSKToBeddows('0.1'),
nonce: this.state.nonce,
});
console.log("========= HELLO ========");
console.dir(transferTransaction);
transferTransaction.sign(networkIdentifier,this.state.passphrase);
console.dir(transferTransaction);
api.transactions.broadcast(transferTransaction.toJSON()).then(response => {
this.setState({response:response});
this.setState({transaction:transferTransaction});
}).catch(err => {
console.log(JSON.stringify(err.errors, null, 2));
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>Transfer</h2>
<p>Send tokens from one account to another.</p>
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<label>
Recipient:
<input type="text" id="address" name="address" onChange={this.handleChange} />
</label>
<label>
Amount (1 = 10^8 tokens):
<input type="text" id="amount" name="amount" onChange={this.handleChange} />
</label>
<label>
Nonce:
<input type="text" id="nonce" name="nonce" onChange={this.handleChange} />
</label>
<label>
Passphrase:
<input type="text" id="passphrase" name="passphrase" onChange={this.handleChange} />
</label>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form>
{this.state.response.meta.status &&
<div>
<pre>Transaction: {JSON.stringify(this.state.transaction, null, 2)}</pre>
<p>Response: {JSON.stringify(this.state.response, null, 2)}</p>
</div>
}
</div>
);
}
}
export default Transfer;Send custom transactions
How to send a custom transaction from a web page.
In the example shown below, a hello transaction is sent.
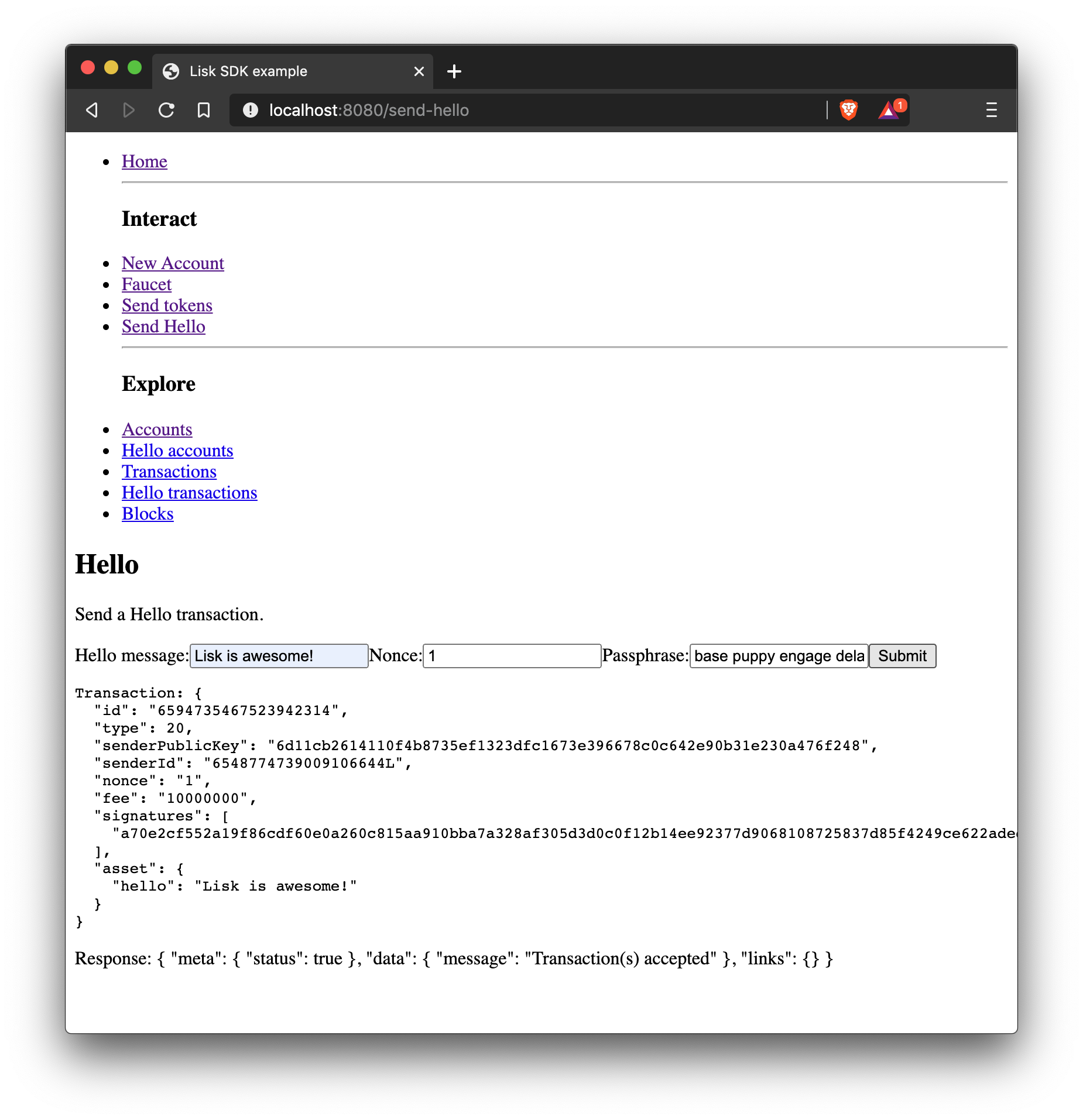
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import {
HelloTransaction,
} from 'lisk-hello-transactions';
import { api } from '../api.js';
import { cryptography } from '@liskhq/lisk-client';
import {utils} from "@liskhq/lisk-transactions";
const networkIdentifier = cryptography.getNetworkIdentifier(
"19074b69c97e6f6b86969bb62d4f15b888898b499777bda56a3a2ee642a7f20a",
"Lisk",
);
class Hello extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
hello: '',
nonce: '',
passphrase: '',
response: { meta: { status: false }},
transaction: {},
};
}
handleChange = (event) => {
let nam = event.target.name;
let val = event.target.value;
this.setState({[nam]: val});
};
handleSubmit = (event) => {
event.preventDefault();
const helloTransaction = new HelloTransaction({
asset: {
hello: this.state.hello,
},
fee: this.state.fee.toString(),
nonce: this.state.nonce.toString(),
});
helloTransaction.sign(networkIdentifier,this.state.passphrase);
if ( helloTransaction.minFee() > helloTransaction.fee) {
this.setState({response:"Please provide a higher fee. Minimum fee for the current transaction: " + helloTransaction.minFee()});
this.setState({transaction:helloTransaction});
} else {
api.transactions.broadcast(helloTransaction.toJSON()).then(response => {
this.setState({response:response});
this.setState({transaction:helloTransaction});
}).catch(err => {
console.log(JSON.stringify(err, null, 2));
});
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>Hello</h2>
<p>Send a Hello transaction.</p>
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<label>
Hello message:
<input type="text" id="hello" name="hello" onChange={this.handleChange} />
</label>
<label>
Nonce:
<input type="text" id="nonce" name="nonce" onChange={this.handleChange} />
</label>
<label>
Passphrase:
<input type="text" id="passphrase" name="passphrase" onChange={this.handleChange} />
</label>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form>
{this.state.response.meta.status &&
<div>
<pre>Transaction: {JSON.stringify(this.state.transaction, null, 2)}</pre>
<p>Response: {JSON.stringify(this.state.response, null, 2)}</p>
</div>
}
</div>
);
}
}
export default Hello;Get all accounts
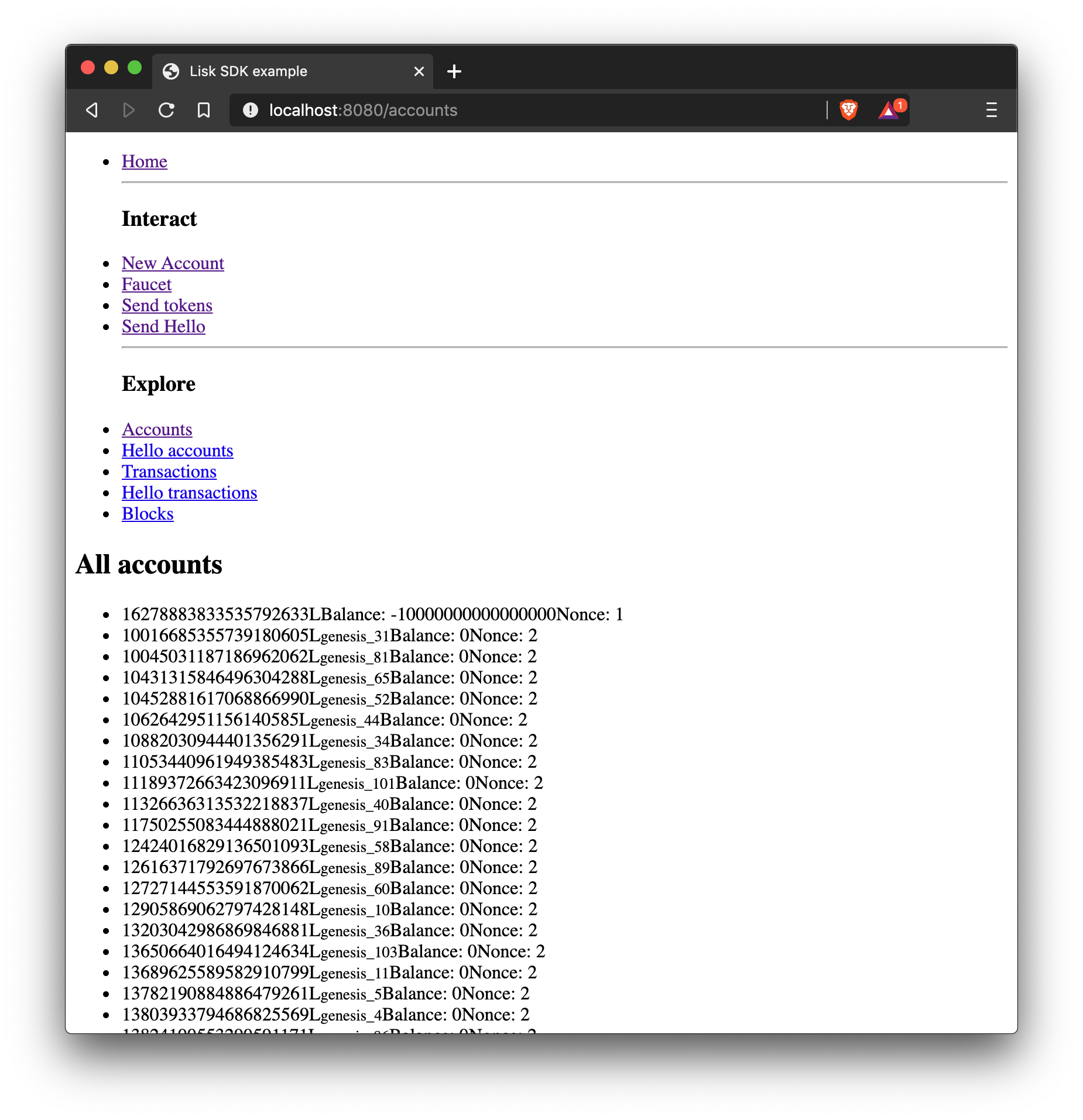
How to display all accounts on a web page.
|
The loop here is implemented in a very basic way to keep it simple. This is adequate for proof of concept applications with a minimal amount of data. However, for production networks, it would be necessary to implement a solution that has the ability to scale with a large amount of data. |
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { api } from '../api.js';
const getData = async () => {
let offset = 0;
let accounts = [];
const accountsArray = [];
do {
const retrievedAccounts = await api.accounts.get({ limit: 100, offset });
accounts = retrievedAccounts.data;
accountsArray.push(...accounts);
if (accounts.length === 100) {
offset += 100;
}
} while (accounts.length === 100);
return accountsArray;
};
class Accounts extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { data: [] };
}
componentDidMount() {
getData().then((data) => {
this.setState({ data });
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>All accounts</h2>
<section>
<ul>
{
this.state.data.map(item => (
<li>
<span>{item.address}</span>
<small>{item.username}</small>
<span>{`Balance: ${item.balance}`}</span>
<span>{`Nonce: ${item.nonce}`}</span>
{/* <pre>{JSON.stringify(this.state.data, null, 2)}</pre> */}
</li>
))
}
</ul>
</section>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Accounts;Get accounts based on asset data
How to display all accounts on a web page.
In the example shown below the accounts are filtered after the existence of the asset.hello property of on account.
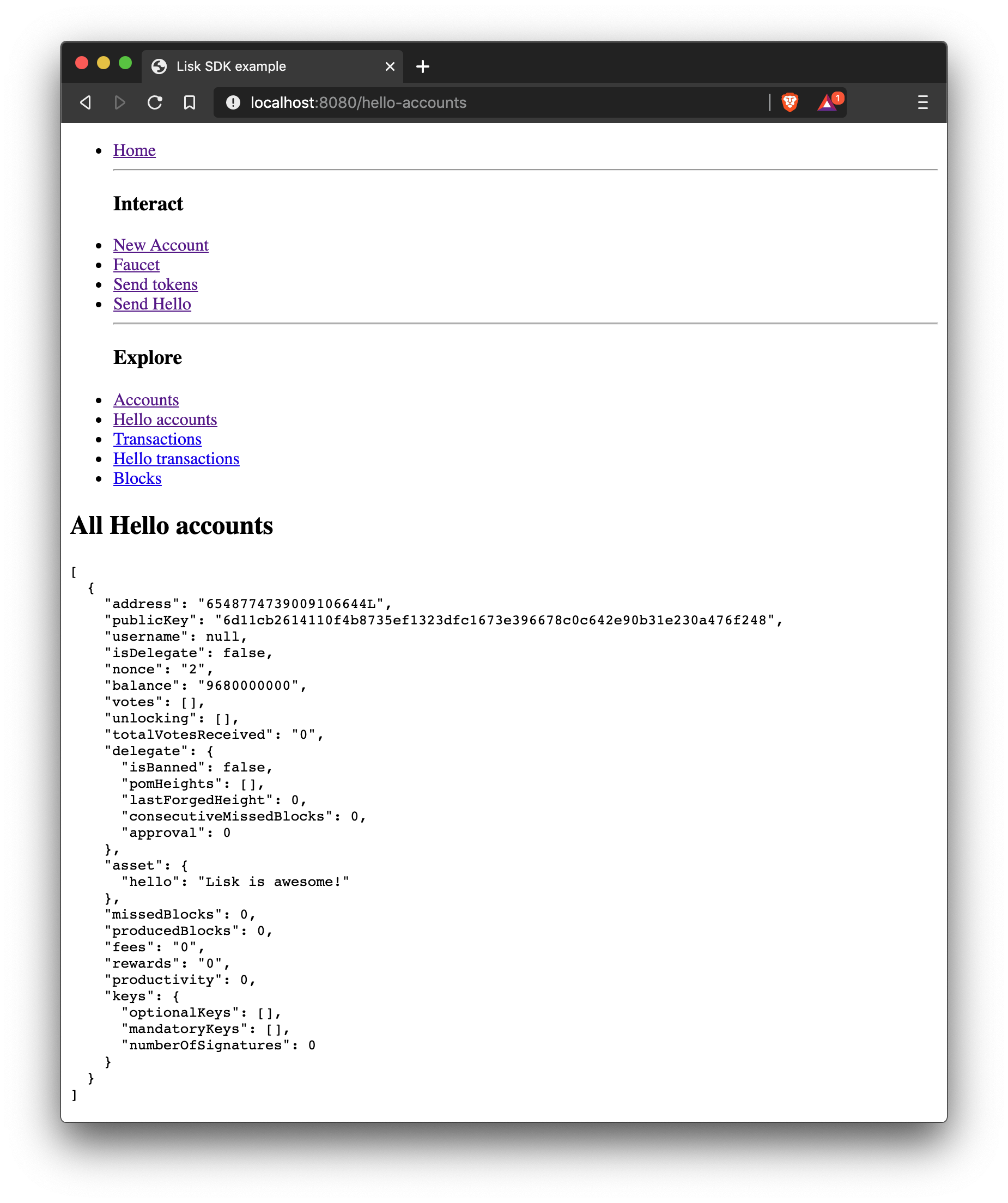
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { api } from '../api.js';
const getData = async () => {
let offset = 0;
let accounts = [];
let accountsArray = [];
do {
const retrievedAccounts = await api.accounts.get({ limit: 100, offset });
accounts = retrievedAccounts.data;
accountsArray.push(...accounts);
if (accounts.length === 100) {
offset += 100;
}
} while (accounts.length === 100);
let assetAccounts = [];
for (var i = 0; i < accountsArray.length; i++) {
let accountAsset = accountsArray[i].asset;
if (accountAsset && Object.keys(accountAsset).indexOf("hello") > -1){
assetAccounts.push(accountsArray[i]);
}
}
return assetAccounts;
}
class HelloAccounts extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { data: [] };
}
componentDidMount() {
getData().then((data) => {
this.setState({ data });
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>All Hello accounts</h2>
<pre>{JSON.stringify(this.state.data, null, 2)}</pre>
</div>
);
}
}
export default HelloAccounts;Get all transactions
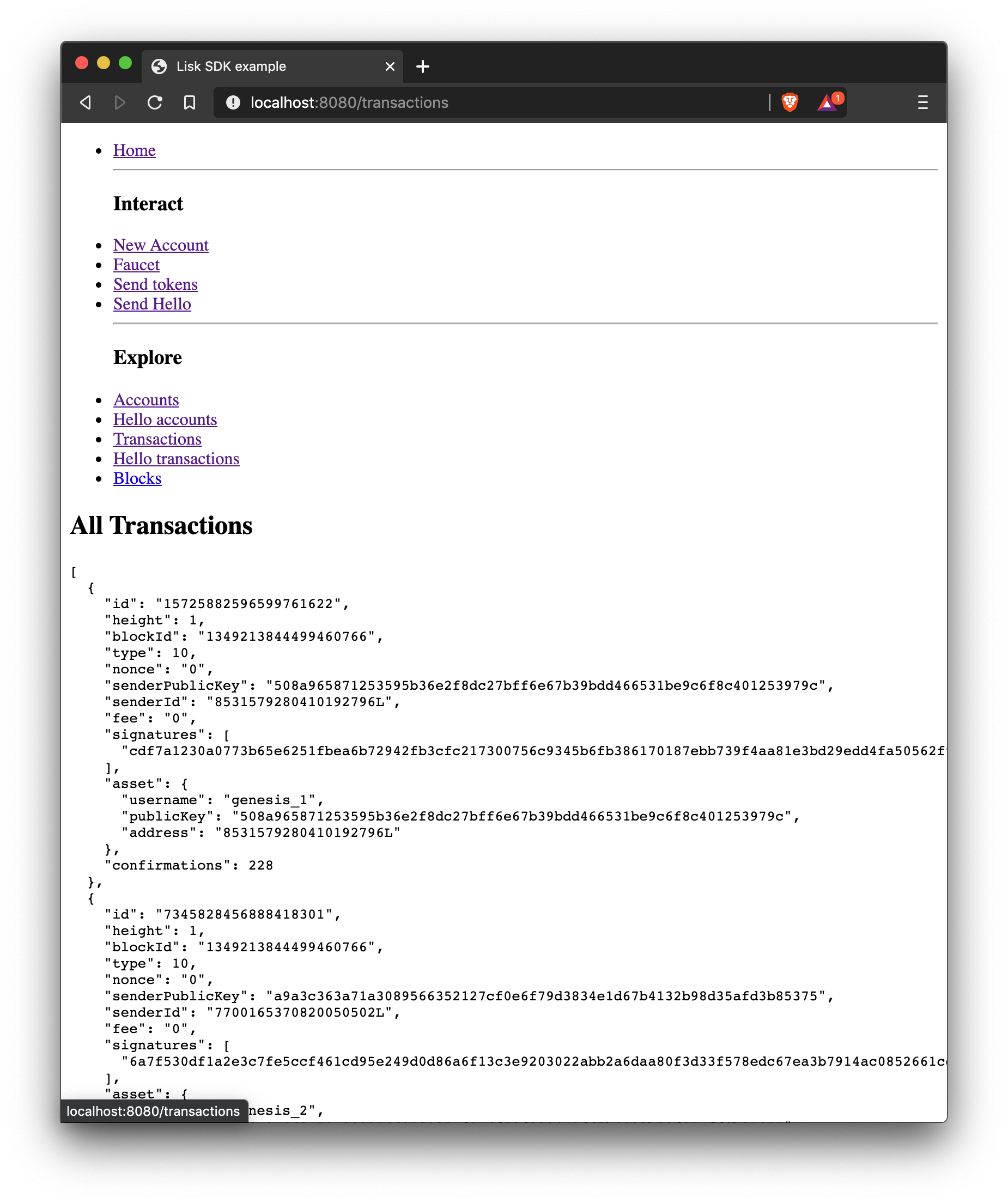
How to display all transactions on a web page.
|
The loop here is implemented in a very basic way to keep it simple. This is adequate for proof of concept applications with a minimal amount of data. However, for production networks, it would be necessary to implement a solution that has the ability to scale with a large amount of data. |
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { api } from '../api.js';
const getData = async () => {
let offset = 0;
let transactions = [];
const transactionsArray = [];
do {
const retrievedTransactions = await api.transactions.get({ limit: 100, offset });
transactions = retrievedTransactions.data;
transactionsArray.push(...transactions);
if (transactions.length === 100) {
offset += 100;
}
} while (transactions.length === 100);
return transactionsArray;
}
class Transactions extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { data: [] };
}
componentDidMount() {
getData().then((data) => {
this.setState({ data });
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>All Transactions</h2>
<pre>{JSON.stringify(this.state.data, null, 2)}</pre>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Transactions;Get transactions by type
How to display all transactions of a particular type on a web page.
In the example shown below, how to filter for hello transactions can be seen.
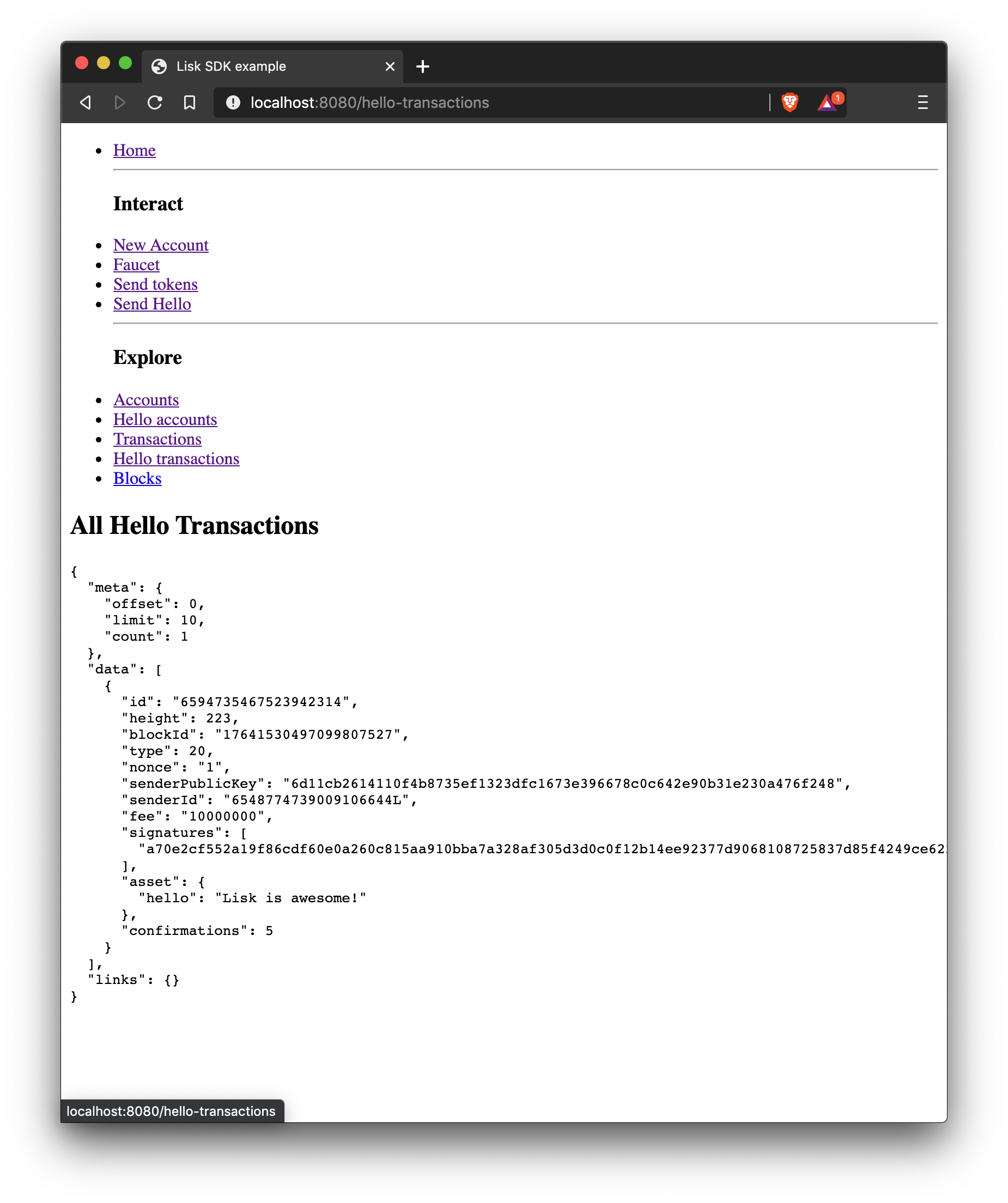
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { api } from '../api.js';
import {
HelloTransaction,
} from 'lisk-hello-transactions';
class HelloTransactions extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { data: [] };
}
componentDidMount() {
api.transactions.get({ type: HelloTransaction.TYPE }).then((data) => {
this.setState({ data });
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>All Hello Transactions</h2>
<pre>{JSON.stringify(this.state.data, null, 2)}</pre>
</div>
);
}
}
export default HelloTransactions;Get all blocks
How to display all blocks on a web page.
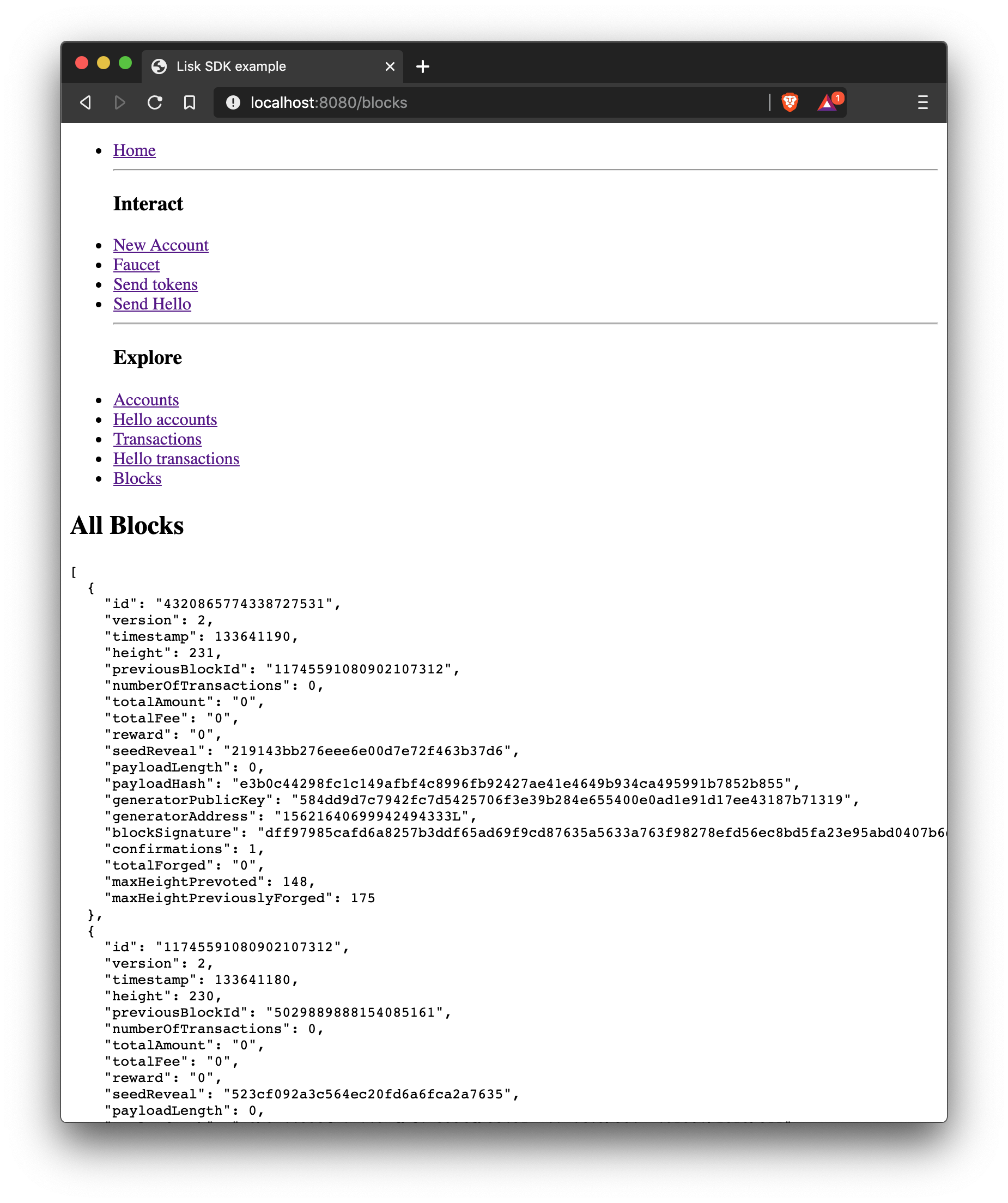
|
The loop here is implemented in a very basic way to keep it simple. This is adequate for proof of concept applications with a minimal amount of data. However, for production networks, it would be necessary to implement a solution that has the ability to scale with a large amount of data. |
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { api } from '../api.js';
const getData = async () => {
let offset = 0;
let blocks = [];
const blocksArray = [];
do {
const retrievedBlocks = await api.blocks.get({ limit: 100, offset });
blocks = retrievedBlocks.data;
blocksArray.push(...blocks);
if (blocks.length === 100) {
offset += 100;
}
} while (blocks.length === 100);
return blocksArray;
}
class Blocks extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { data: [] };
}
componentDidMount() {
getData().then((data) => {
this.setState({ data });
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>All Blocks</h2>
<pre>{JSON.stringify(this.state.data, null, 2)}</pre>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Blocks;