How to implement cross-chain communication
In this chapter, you’ll learn how to:
-
Create CCM inside a command
-
Execute a CCM inside a cc_command
-
Test the implementation of an interoperable module by running the interop example scripts.
If a Lisk app intends to interact with other blockchains in the network, it needs to provide the required cross-chain commands that create and execute the corresponding CCMs.
| To learn more about how sidechains communicate with each other via CCM, check out the page about Cross-chain communication. |
To show how interoperable modules are implemented, we will extend the Hello app with a very simple command, allowing other chains to react to Hello messages.
To keep it simple, the example only implements one reaction type: Likes.
The example can be extended to include more reaction types such as likes, dislikes, or replies for Hello messages if desired.
1. Creating interoperable modules
If two sidechains intend to interact with each other, for example, if sidechain A wishes to utilize services that sidechain B provides, this can be achieved via interoperable modules.
In this context, sidechain A would be the sending chain, and sidechain B would be the receiving chain.
To achieve cross-chain communication, the two sidechains need to fulfill the following requirements:
-
Both the sending and the receiving chains need to be registered as sidechains to the same mainchain.
-
Both the sending and the receiving chains need to be active sidechains, with at least one relayer node connected to the mainchain.
-
The sending chain needs to implement a module command that creates and sends a CCM.
-
The receiving chain needs to implement a module cc_command that accepts and executes the CCM.
| The interop example contains a complete interoperable set up for you to try out. If you simply want to try it out, refer to the next section Testing interoperable modules. |
To learn the details about the implementation of the required module commands, check out the following dedicated guides:
2. Testing interoperable modules
As the interaction between two sidechains always involves three chains (sending chain, receiving chain, and mainchain), it is quite complicated to test newly implemented interoperable modules locally.
To simplify the process, the lisk-sdk provides useful example scripts that can be easily adjusted to try out new interoperable modules.
2.1. The interop example of the lisk-sdk repository
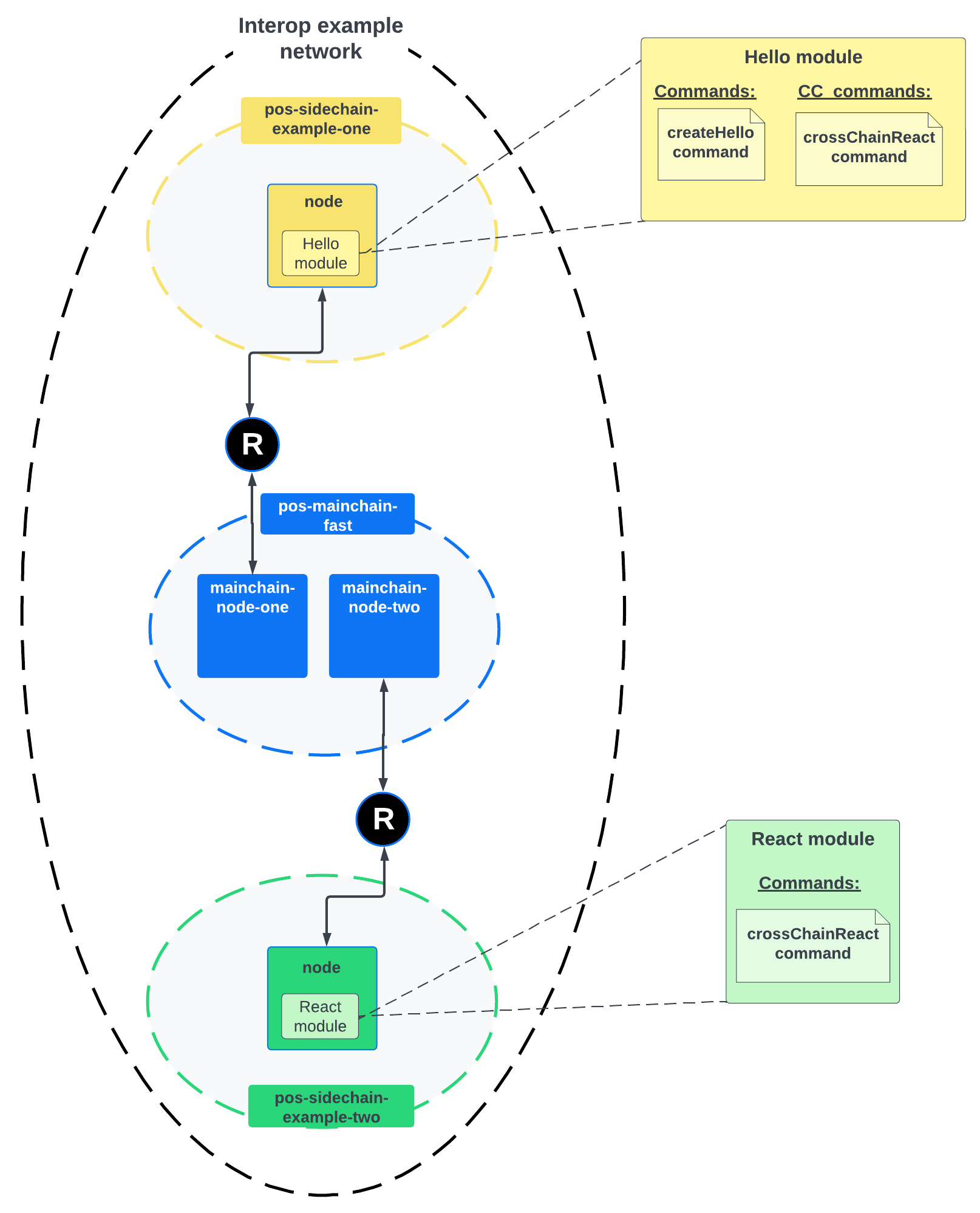
To try out the cross-chain communication of interoperable modules locally, go to the interop/example in the lisk-sdk repository.
There, you find a README.md which describes all the required steps to set up a simple interoperability example, as illustrated in Figure 1.
Additionally, you find examples of how to execute cross-chain token transfers between the chains.
To start the interoperability example, run the start_example script.
./start_exampleThis will install all required dependencies, start all sidechain and mainchain nodes and register them with each other.
Observe the console logs to verify that all steps are executed successfully without errors.
2.1.1. Verify the sidechain account is funded with mainchain tokens
The account sending the crossChainReact command, who will create a new CCM, needs to provide the fees for the execution of the CCM in tokens that are native on the mainchain.
This is why it should be verified, that the account, that intends to send the transaction, owns enough mainchain tokens.
Run the following script to perform a cross chain transfer from the mainchain to sidechain 2:
ts-node pos-mainchain-fast/config/scripts/transfer_lsk_sidechain_two.ts| Wait for a few moments until you check the Balance on sidechain 2, as the cross-chain transfer can take some time |
Verify the account intending to send the CCM has enough balance to pay the transaction & CCM fees:
./bin/run endpoint:invoke token_getBalances '{"address":"lskx5uqu2zzybdwrqswd8c6b5v5aj77yytn4k6mv6"}' --prettyAs the response shows, the account has now more than enough sidechain and mainchain tokens to pay the required fees.
{
"balances": [
{
"tokenID": "0400000000000000",
"availableBalance": "910000000000",
"lockedBalances": []
},
{
"tokenID": "0400000200000000",
"availableBalance": "100000000000000",
"lockedBalances": []
}
]
}2.2. Create a Hello message on sidechain 1
Now, as it is verified, that the sending account has enough tokens to pay the fees for the transaction and the CCM, we can proceed to send a new Hello message on sidechain 1.
Navigate into the folder pos-sidechain-example-one and use the node CLI to create a new Hello message.
./bin/run transaction:create hello createHello 10000000 --json --pretty --key-derivation-path="m/44'/134'/12'" --sendYou will be prompted for the accounts' passphrase.
Sign the transaction with the passphrase stored in passphrase.json in the config folder.
? Please enter passphrase: [hidden]
Next, you will be prompted for a Hello message. This can be any string with a minimum length of 3 and a maximum of 256 characters.
? Please enter: message: Hello sidechain 2! :-)
Because we added the --json flag to the command, the transaction is also printed in human-readable JSON format, which allows us to verify all properties of the transaction again.
The --pretty flag formats the JSON with proper indents.
{
"transaction": {
"module": "hello",
"command": "createHello",
"fee": "10000000",
"nonce": "0",
"senderPublicKey": "3e8ba5794c323cc83c4085576930aa5a49486f989498f15980dc2c50e125226f",
"signatures": [
"5060ccd88c2083a3a3905c65055804adf2ec9a9f30e7ebd88f29e42ff0dadd4c18ba9dbc462f2305c041bec68e498f8922941758cd0403766c89c7199af84408"
],
"params": {
"message": "Hello sidechain 2! :-)"
},
"id": "cbd493f4e554c4ffde09a8a0d641164439d5ef9e7605c84d52d2d25248a897a7"
}
}Because we added the --send flag to the transaction:create command, the transaction is sent to the node directly, after it is created.
The node should respond with the corresponding transaction ID if it accepts the transaction.
Transaction with id: 'cbd493f4e554c4ffde09a8a0d641164439d5ef9e7605c84d52d2d25248a897a7' received by node.
2.2.1. Get the Hello message
To verify that the Hello message was in fact created on the blockchain, use the hello_getHello endpoint to get the Hello message for the sending account:
./bin/run endpoint:invoke hello_getHello '{"address":"lskmjwp8z88avvxn4voktmx8cu9wk4opjkna5owt5"}'If all works correctly, the node should respond with the Hello message that was created in the previous step.
{"message":"Hello sidechain 2! :-)"}2.3. Create Reaction on sidechain 2
Now that a Hello message exists on sidechain 1, we want to react to this message with an account on sidechain 2.
For this, the user who wishes to react will send a transaction on sidechain 2.
This transaction will create a CCM which is collected by a relayer, and posted to the mainchain. On the mainchain, it is collected again by a relayer, and posted to the receiving chain, which is sidechain 1 in this case.
To observe the cross-chain communication, please open the Dashboards for sidechain 1 and sidechain 2 in the browser.
- Dashboards
-
-
Sidechain 1: http://localhost:4006
-
Sidechain 2: http://localhost:4007
-
Scroll down on the Dashboards to the "Events" section, and filter for the following events: CCM Processed, CCMSendSuccess, CCMSentFailed
Additionally, it can be beneficial to also observe the logs of the different sidechain nodes. Open two different terminal windows and display the live node logs inside:
- Logs
-
-
Sidechain 1:
pm2 log 2 -
Sidechain 2:
pm2 log 3
-
Now, in a third terminal window, run the following command to create and directly send a reaction to the Hello message on sidechain 1.
We define the following params:
-
reactionType: The type of the reactions represented as an integer. We have only implemented type 0 in the example, which represents a like, so we choose0here. -
helloMessageID: We use the address of the account that created the Hello message to identify the Hello message. -
receivingChainID: Chain ID of the receiving chain (= Sidechain 1 in this example). This property is required to create the CCM. -
messageFee: Fee that is paid for the execution of the CCM. This property is required to create the CCM. -
messageFeeTokenID: Token ID of the tokens being used to pay themessageFee. By default, this is the Token ID of the native mainchain Token. This property is required to create the CCM.
./bin/run transaction:create react crossChainReact 1000000 --json --pretty --key-derivation-path="m/44'/134'/12'" --params='{"reactionType":0,"helloMessageID":"lskmjwp8z88avvxn4voktmx8cu9wk4opjkna5owt5","receivingChainID":"04000001","data":"","messageFee":"2100000","messageFeeTokenID":"0400000000000000"}' -p "crack tide merry unit rival joke drum private object top obey twelve exit scale sure pipe apple view forward surge aspect farm meat farm" --send
In the above example, we provide the passphrase directly in the command via the -p flag, therefore we are not prompted for the passphrase, and the transaction is signed directly.
|
{
"transaction": "0a057265616374120f726561637443726f7373436861696e180020c0843d2a20c94952af78216ff92d615f4eb566726693d05df2d0b82f7fce26fc1f0e6e8724323a080012296c736b6d6a7770387a3838617676786e34766f6b746d7838637539776b346f706a6b6e61356f7774351a0022040400000128a09680013a404f68f83f8e32aadba4b2bb465ac0b09ca6a1c0ca247750e21d22cbd0fc53a5684fc3d4185d47e69e6e85a818ef04a61430dcadc096813cb205f735d04e3c4901"
}{
"transaction": {
"module": "react",
"command": "crossChainReact",
"fee": "1000000",
"nonce": "0",
"senderPublicKey": "c94952af78216ff92d615f4eb566726693d05df2d0b82f7fce26fc1f0e6e8724",
"signatures": [
"4f68f83f8e32aadba4b2bb465ac0b09ca6a1c0ca247750e21d22cbd0fc53a5684fc3d4185d47e69e6e85a818ef04a61430dcadc096813cb205f735d04e3c4901"
],
"params": {
"reactionType": 0,
"helloMessageID": "lskmjwp8z88avvxn4voktmx8cu9wk4opjkna5owt5",
"receivingChainID": "04000001",
"data": "",
"messageFee": "2100000"
},
"id": "5043174c97f508b711d9be0ec57ed60009ea83b57b2a665cef8c99420b9fcbb2"
}
}If the node accepts the transaction, it should respond with the corresponding transaction ID.
Transaction with id: '5043174c97f508b711d9be0ec57ed60009ea83b57b2a665cef8c99420b9fcbb2' received by node.
2.4. Observe the execution of the CCM
Now go directly to the Dashboard events of sidechain 2 and look for the following event:
If you see the ccmSendSuccess event in the events logs, it means, the CCM was sent successfully on sidechain 2.
interoperability_ccmSendSuccess (height: 772 index: 8 topics: 045043174c97f508b711d9be0ec57ed60009ea83b57b2a665cef8c99420b9fcbb2, 04000002, 04000001, 5fc4e869feb87e83801adee1c5ca44a9c71fa10b6668021abed48d73864bd69f)
{
"ccm": {
"module": "hello",
"crossChainCommand": "crossChainReact",
"nonce": "1",
"fee": "2100000",
"sendingChainID": "04000002",
"receivingChainID": "04000001",
"params": "080012296c736b6d6a7770387a3838617676786e34766f6b746d7838637539776b346f706a6b6e61356f7774351a00",
"status": 0
}
}Next, go to the events of the Dashboard of sidechain 1 and look for the following event:
interoperability_ccmProcessed (height: 335 index: 3 topics: ab36b23bce5e2a0cebe9131c5b3bddfd8132e9367f1cf9a95875ae74b8ca3909, f092606d704d8a205bf2d702119c4761e3cb8cc22197fd28411f28fae9aa4d98, 04000002, 04000001)
{
"ccm": {
"module": "hello",
"crossChainCommand": "crossChainReact",
"nonce": "1",
"fee": "100000000",
"sendingChainID": "04000002",
"receivingChainID": "04000001",
"params": "080112296c736b367134747a79657633386666776d66756263746163717a6f667962377a326f667266666d33791a0772656163746564",
"status": 0
},
"result": 0,
"code": 0
}If there is an event similar to the above example, it means that the CCM from sidechain 2 was successfully processed on sidechain 1.
Once the CCM is received and executed on the node, it is possible to request the reaction on sidechain 1 with the endpoint hello_getReactions which we implement in the section Creating a new endpoint for getting reactions for a Hello message.
./bin/run endpoint:invoke hello_getReactions '{"address":"lskmjwp8z88avvxn4voktmx8cu9wk4opjkna5owt5"}'{"reactions":{"likes":[{"type":"Buffer","data":[128,101,154,216,166,239,226,225,198,252,61,66,236,115,108,201,97,49,120,140]}]}}
By receiving this response from the blockchain store of sidechain 1, it is verified that the cross-chain reaction to Hello messages was implemented successfully.
2.5. Tips for debugging the interoperability example
Remember to adjust the value --data-path to the correct path for the respective node.
The endpoints can be invoked from any node CLI, and will always respond with data from the node specified in the data-path.
|
2.5.1. How to get the last sent CCM
To get the last sent CCM on a chain, invoke the chainConnector_getLastSentCCM endpoint.
./bin/run endpoint:invoke chainConnector_getLastSentCCM --pretty --data-path=~/.lisk/mainchain-node-one2.5.2. How to authorize the chain connector plugin
In case it is necessary to restart the nodes, it is necessary to manually authorize the chain connector plugin again. Otherwise, it will not be possible to send CCUs between chains.
./bin/run endpoint:invoke 'chainConnector_authorize' '{"password": "lisk", "enable": true }' --data-path=~/.lisk/pos-sidechain-example-two./bin/run endpoint:invoke 'chainConnector_authorize' '{"password": "lisk", "enable": true }' --data-path=~/.lisk/pos-sidechain-example-one./bin/run endpoint:invoke 'chainConnector_authorize' '{"password": "lisk", "enable": true }' --data-path=~/.lisk/mainchain-node-one./bin/run endpoint:invoke 'chainConnector_authorize' '{"password": "lisk", "enable": true }' --data-path=~/.lisk/mainchain-node-two2.5.3. How to reset the interoperability example
To completely reset the interop example, and start fresh, there is a very handy command which will perform all the necessary steps for you:
./start_example --reset2.5.4. How to monitor the nodes
This small script monitors the connections between mainchain and sidechain nodes.
./monitorCaptured At: 12:49:26 - Mainchain_1: "sidechain_example_one" : Height: 10 | Status: 1 "sidechain_example_two" : Height: 10 | Status: 1 - Mainchain_2: "sidechain_example_one" : Height: 10 | Status: 1 "sidechain_example_two" : Height: 10 | Status: 1 - Sidechain_1: "lisk_mainchain" : Height: 10 | Status: 1 - Sidechain 2: "lisk_mainchain" : Height: 10 | Status: 1